Xiao Fan (范潇)
Senior student @ Tongji University
Interests: Test-time Adaptation, Self-Evolving Embodied Agent
xiaofan140@gmail.com · Google Scholar · GitHub · WeChat · CV
Education¶
| Degree | Institution | Advisor | Years |
|---|---|---|---|
| B.Eng. in Data Science | Tongji University | 2022–2026 | |
| D.Eng in Electronic Information | Tsinghua University | Prof. Zhi Wang | 2026–2031 |
Recent News
- [2025-09] My personal website is launched!
- [2025-09] We have released a new paper VERL on Reinforcement Learning for reasoning LLM.
- [2025-11] My first paper is accepted by AAAI 2026 (CCF-A, 17.6% overall acceptance rate)!
Publications¶
* equal contribution, † corresponding author.
2025¶
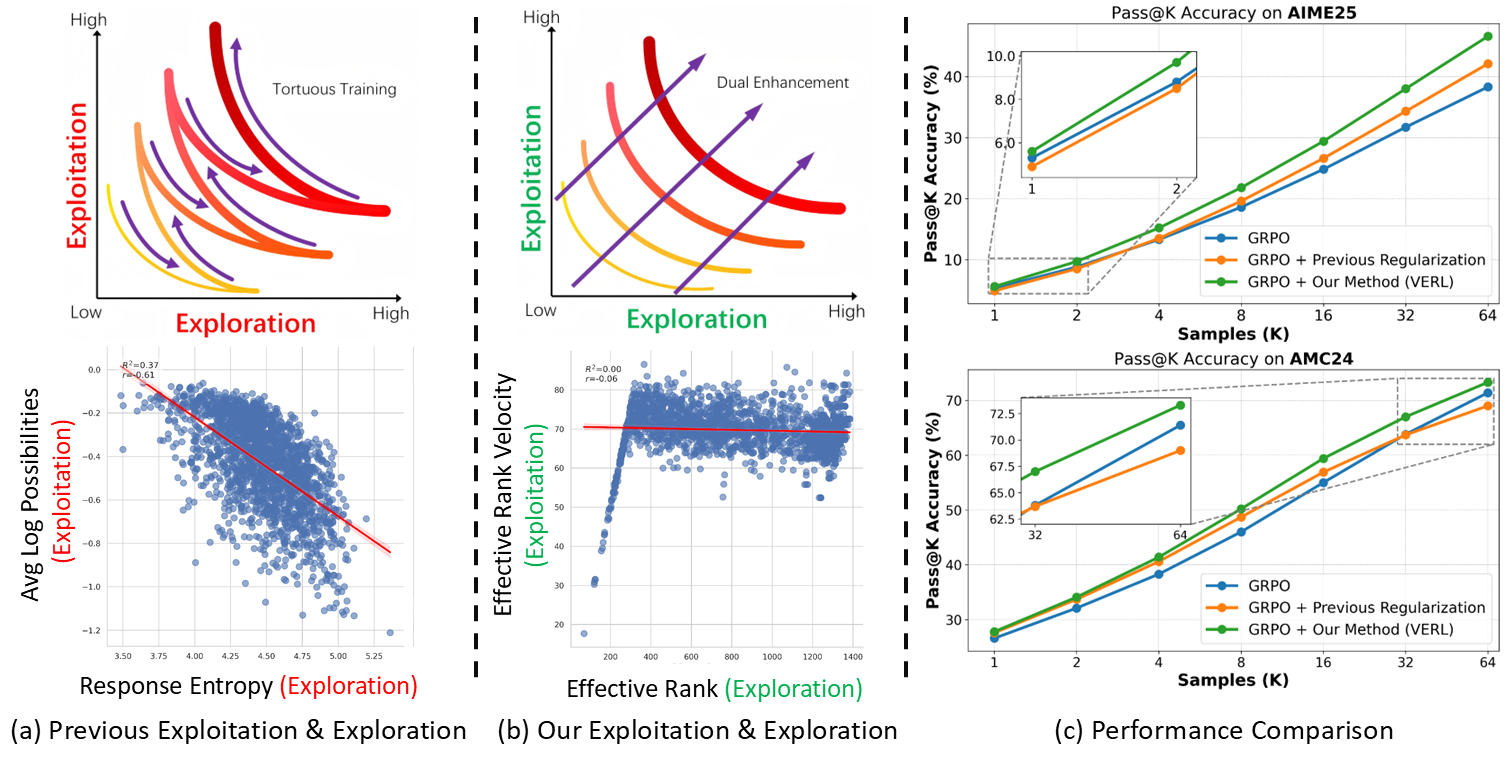 Beyond the Exploration-Exploitation Trade-off: A Hidden State Approach for LLM Reasoning in RLVR
Beyond the Exploration-Exploitation Trade-off: A Hidden State Approach for LLM Reasoning in RLVR
Fanding Huang*, Guanbo Huang*, Xiao Fan, Yi He, Xiao Liang, Xiao Chen, Qinting Jiang, Faisal Nadeem Khan, Jingyan Jiang†, Zhi Wang†.
Submitted to ACL ARR 2026.
[Paper] [Code] [Project] [BibTex]
Abstract
A prevailing view in Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) interprets recent progress through the lens of an exploration-exploitation trade-off, a perspective largely shaped by token-level metrics. We re-examine this perspective, proposing that this perceived trade-off may not be a fundamental constraint but rather an artifact of the measurement level. To investigate this, we shift the analysis to the semantically rich hidden-state space, adopting Effective Rank (ER) to quantify exploration and proposing its novel first- and second-order derivatives, named ER Velocity and ER Acceleration, to capture exploitation dynamics. Our analysis reveals that in the semantic space, exploration and exploitation could be decoupled (Sec.4). This finding reveals an opportunity to enhance both capacities simultaneously. This insight motivates our method, Velocity-Exploiting Rank-Learning (VERL), the first to operationalize the principle of synergistic exploration-exploitation enhancement by directly shaping the RL advantage function. The key innovation is leveraging the theoretically stable ERA as a predictive meta-controller to create a synergistic, dual-channel incentive structure. Instead of forcing a trade-off, VERL prospectively amplifies rewards for exploration to preempt overconfidence and reinforces exploitative gains to consolidate reasoning. Experiments across diverse LLMs and reasoning benchmarks show consistent gains, including up to 21.4% absolute accuracy improvement on the challenging Gaokao 2024 dataset.
2026¶
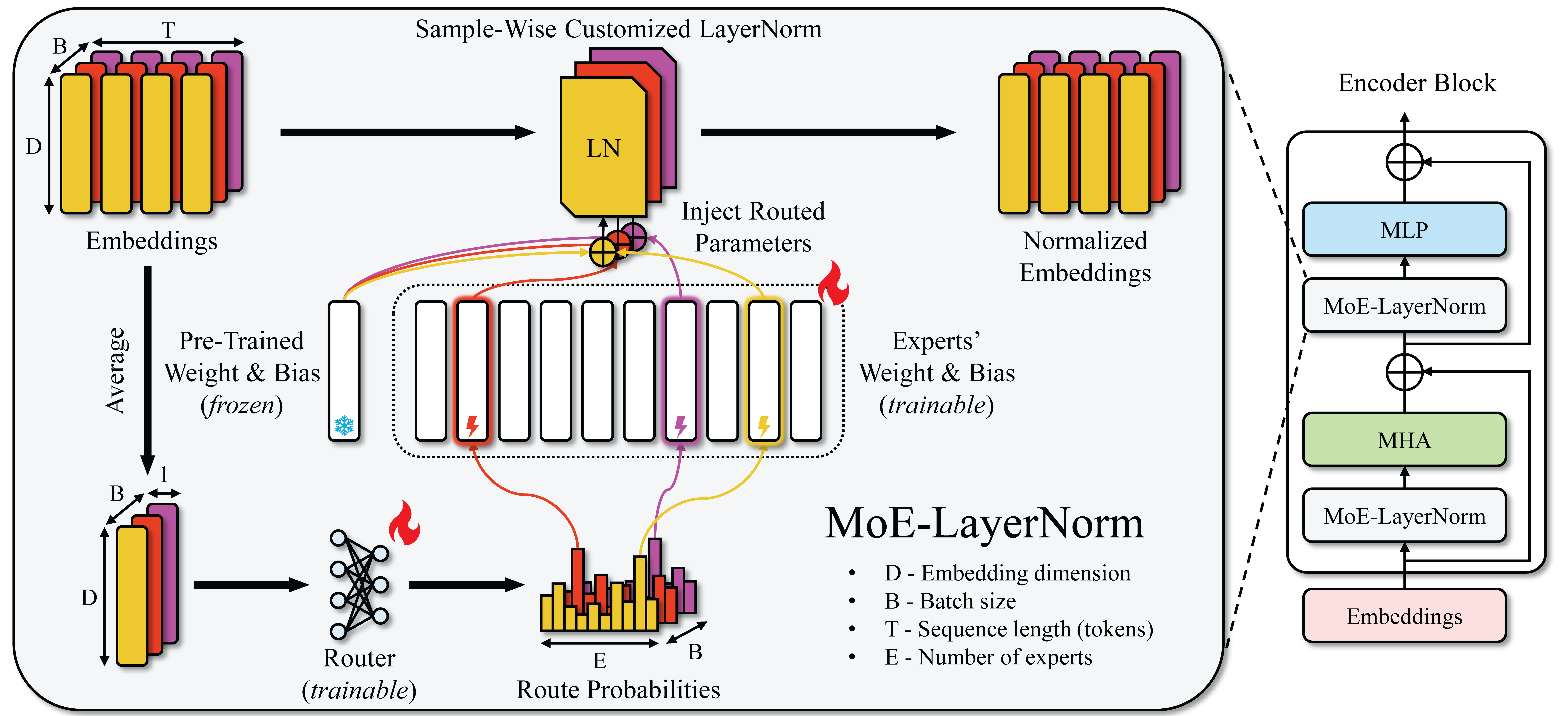
MoETTA: Test-Time Adaptation Under Mixed Distribution Shifts with MoE-LayerNorm
Xiao Fan, Jingyan Jiang†, Zhaoru Chen, Fanding Huang, Xiao Chen, Qinting Jiang, Bowen Zhang, Xing Tang, Zhi Wang.
Accepted by AAAI 2026 (CCF-A, 17.6% overall acceptance rate).
[Paper] [Code] [BibTex]
Abstract
Test-Time Adaptation (TTA) has proven effective in mitigating performance drops under single-domain distribution shifts by updating model parameters during inference. However, real-world deployments often involve mixed distribution shifts, where test samples are affected by diverse and potentially conflicting domain factors, posing significant challenges even for state-of-the-art TTA methods. A key limitation in existing approaches is their reliance on a unified adaptation path, which fails to account for the fact that optimal gradient directions can vary significantly across different domains. Moreover, current benchmarks focus only on synthetic or homogeneous shifts, failing to capture the complexity of real-world heterogeneous mixed distribution shifts. To address this, we propose MoETTA, a novel entropy-based TTA framework that integrates the Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture. Rather than enforcing a single parameter update rule for all test samples, MoETTA introduces a set of structurally decoupled experts, enabling adaptation along diverse gradient directions. This design allows the model to better accommodate heterogeneous shifts through flexible and disentangled parameter updates. To simulate realistic deployment conditions, we introduce two new benchmarks: potpourri and potpourri+. While classical settings focus solely on synthetic corruptions (i.e., ImageNet-C), potpourri encompasses a broader range of domain shifts—including natural, artistic, and adversarial distortions—capturing more realistic deployment challenges. Additionally, potpourri+ further includes source-domain samples to evaluate robustness against catastrophic forgetting. Extensive experiments across three mixed distribution shifts settings show that MoETTA consistently outperforms strong baselines, establishing new state-of-the-art performance and highlighting the benefit of modeling multiple adaptation directions via expert-level diversity.
Projects¶
- I promise I will soon organize and share my past projects.
Service¶
- Sadly, nothing to serve yet.